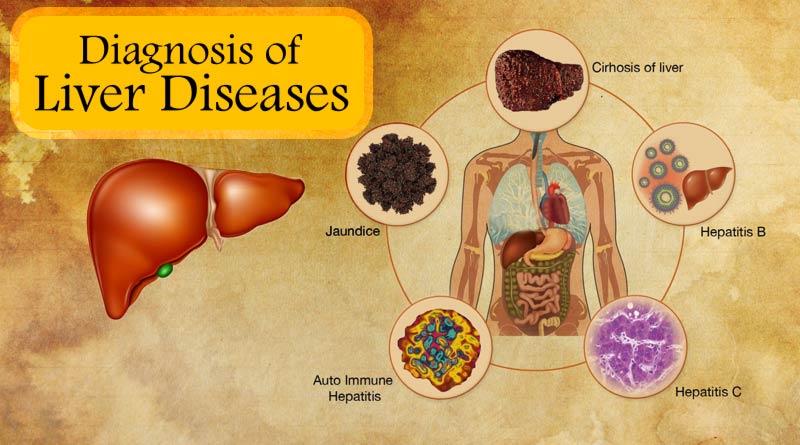
Diagnosis of liver diseases
The precise diagnosis of liver diseases involves a history and physical examination performed by a health care professional. Understanding the symptoms and the patient’s risk factors for liver disease will help guide any diagnostic tests that may be considered.
Sometimes history is difficult, especially in patients who abuse alcohol. These patients tend to minimize their consumption, and it is often family members who are able to provide the correct information.
Liver disease can have physical findings that affect almost all body systems including the heart, lungs, abdomen, skin, brain and cognitive function, and other parts of the nervous system. The physical examination often requires evaluation of the entire body.
Blood tests are helpful in assessing liver inflammation and function.
Specific liver function blood tests include:
- AST and ALT ( transaminase chemicals released with liver cell inflammation);
- GGT and alkaline phosphatase (chemicals released by cells lining the bile ducts);
- bilirubin; and
- Protein and albumin levels.
Other blood tests may be considered, including the following:
- Complete blood count (CBC), patients with end stage liver disease may have bone marrow suppression and low red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. As a result, patients with cirrhosis may have bleeding;
- INR blood clotting function may be impaired due to poor protein production and is a sensitive measure of liver function;
- lipase to check for pancreas inflammation;
- electrolytes, BUN andcreatinine to assess kidney function; and
- ammonia blood level assessment is helpful in patients with mental confusion to determine whether liver failure is a potential cause.
Imaging studies may be used to visualize, not only the liver, but other nearby organs that may be diseased. Examples of imaging studies include:
- CT scan (computerized axial tomography),
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), and
- Ultrasound (sound wave imaging, which is especially helpful in assessing the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Liver biopsy may be considered to confirm a specific diagnosis of liver disease. Under local anesthetic, a long thin needle is inserted through the chest wall into the liver, where a small sample of liver tissue is obtained for examination under a microscope.
 Parsi Teb Physical and Mental Health Journal
Parsi Teb Physical and Mental Health Journal